matplotlib.pyplot.show#
- matplotlib.pyplot.show(*, block=None)[source]#
Display all open figures.
- Parameters:
- blockbool, optional
Whether to wait for all figures to be closed before returning.
If
Trueblock and run the GUI main loop until all figure windows are closed.If
Falseensure that all figure windows are displayed and return immediately. In this case, you are responsible for ensuring that the event loop is running to have responsive figures.Defaults to True in non-interactive mode and to False in interactive mode (see
pyplot.isinteractive).
See also
Notes
Saving figures to file and showing a window at the same time
If you want an image file as well as a user interface window, use
pyplot.savefigbeforepyplot.show. At the end of (a blocking)show()the figure is closed and thus unregistered from pyplot. Callingpyplot.savefigafterwards would save a new and thus empty figure. This limitation of command order does not apply if the show is non-blocking or if you keep a reference to the figure and useFigure.savefig.Auto-show in jupyter notebooks
The jupyter backends (activated via
%matplotlib inline,%matplotlib notebook, or%matplotlib widget), callshow()at the end of every cell by default. Thus, you usually don't have to call it explicitly there.
Examples using matplotlib.pyplot.show#
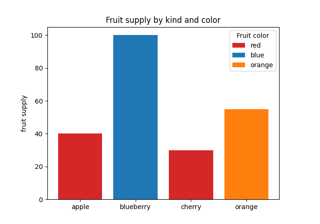
Plotting categorical variables
Plotting the coherence of two signals
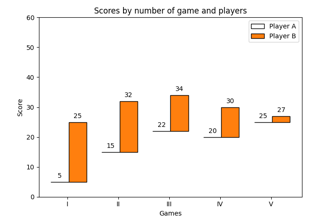
Discrete distribution as horizontal bar chart
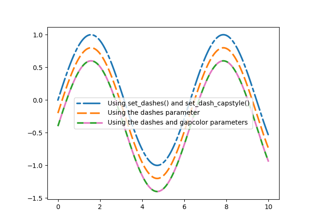
Customizing dashed line styles
Lines with a ticked patheffect
Plotting masked and NaN values
Mapping marker properties to multivariate data
Scatter plots with custom symbols
Creating a timeline with lines, dates, and text
Cross- and Auto-Correlation Demo
Interactive Adjustment of Colormap Range
Colormap Normalizations SymLogNorm
Contouring the solution space of optimizations
Blend transparency with color in 2D images
Modifying the coordinate formatter
Contour plot of irregularly spaced data
Advanced quiver and quiverkey functions
Controlling view limits using margins and sticky_edges
Resizing axes with constrained layout
Resizing axes with tight layout
Different scales on the same axes
Figure size in different units
Figure labels: suptitle, supxlabel, supylabel
Combining two subplots using subplots and GridSpec
Using Gridspec to make multi-column/row subplot layouts
Managing multiple figures in pyplot
Creating multiple subplots using plt.subplots
Percentiles as horizontal bar chart
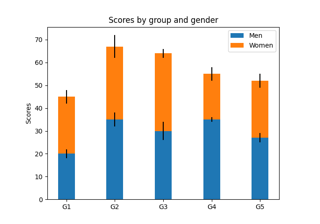
Artist customization in box plots
Box plots with custom fill colors
Box plot vs. violin plot comparison
Plot a confidence ellipse of a two-dimensional dataset
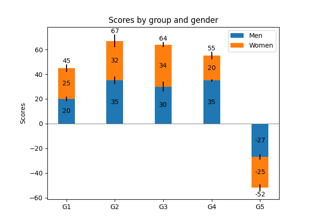
Different ways of specifying error bars
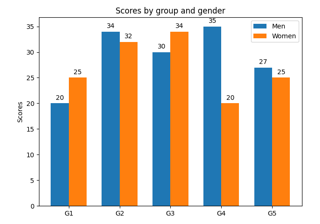
Including upper and lower limits in error bars
Creating boxes from error bars using PatchCollection
Using histograms to plot a cumulative distribution
Some features of the histogram (hist) function
Demo of the histogram function's different histtype settings
The histogram (hist) function with multiple data sets
Producing multiple histograms side by side
Using accented text in Matplotlib
The difference between \dfrac and \frac
Labeling ticks using engineering notation
Annotation arrow style reference
Using a ttf font file in Matplotlib
Fonts demo (object-oriented style)
Fonts demo (keyword arguments)
Legend using pre-defined labels
Rendering math equations using TeX
Controlling style of text and labels using a dictionary
Default text rotation demonstration
Text Rotation Relative To Line
Programmatically controlling subplot adjustment
Colors in the default property cycle
Creating a colormap from a list of colors
Reference for Matplotlib artists
Line, Poly and RegularPoly Collection with autoscaling
Bayesian Methods for Hackers style sheet
Showing RGB channels using RGBAxes
Adding a colorbar to inset axes
Controlling the position and size of colorbars with Inset Axes
Per-row or per-column colorbars
Axes with a fixed physical size
Setting a fixed aspect on ImageGrid cells
Make room for ylabel using axes_grid
Scatter Histogram (Locatable Axes)
mpl_toolkits.axisartist.floating_axes features
Integral as the area under a curve
Shaded & power normalized rendering
Animated image using a precomputed list of images
Pausing and Resuming an Animation
Figure/Axes enter and leave events
Changing colors of lines intersecting a box
Building histograms using Rectangles and PolyCollections
Create 2D bar graphs in different planes
Demonstrates plotting contour (level) curves in 3D
Demonstrates plotting contour (level) curves in 3D using the extend3d option
Projecting contour profiles onto a graph
Projecting filled contour onto a graph
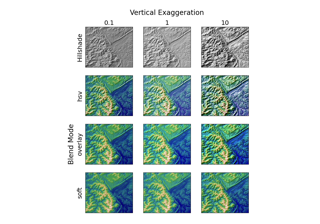
Custom hillshading in a 3D surface plot
Create 3D histogram of 2D data
Generate polygons to fill under 3D line graph
3D surface with polar coordinates
Triangular 3D filled contour plot
3D voxel plot of the numpy logo
3D voxel / volumetric plot with rgb colors
3D voxel / volumetric plot with cylindrical coordinates
3D wireframe plots in one direction
Radar chart (aka spider or star chart)
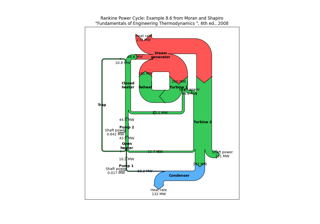
Long chain of connections using Sankey
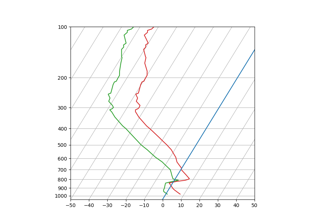
SkewT-logP diagram: using transforms and custom projections
Automatically setting tick positions
Centering labels between ticks
Formatting date ticks using ConciseDateFormatter
Placing date ticks using recurrence rules
Set default y-axis tick labels on the right
Setting tick labels from a list of values
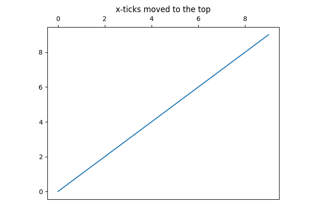
Move x-axis tick labels to the top
Connection styles for annotations
Select indices from a collection using polygon selector
Thresholding an Image with RangeSlider
Rectangle and ellipse selectors
Snapping Sliders to Discrete Values
Customizing Matplotlib with style sheets and rcParams
Arranging multiple Axes in a Figure
Faster rendering by using blitting
Creating Colormaps in Matplotlib
Choosing Colormaps in Matplotlib