matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm#
- class matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm(boundaries, ncolors, clip=False, *, extend='neither')[source]#
Bases:
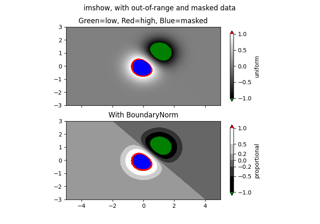
NormalizeGenerate a colormap index based on discrete intervals.
Unlike
NormalizeorLogNorm,BoundaryNormmaps values to integers instead of to the interval 0-1.- Parameters:
- boundariesarray-like
Monotonically increasing sequence of at least 2 bin edges: data falling in the n-th bin will be mapped to the n-th color.
- ncolorsint
Number of colors in the colormap to be used.
- clipbool, optional
If clip is
True, out of range values are mapped to 0 if they are belowboundaries[0]or mapped toncolors - 1if they are aboveboundaries[-1].If clip is
False, out of range values are mapped to -1 if they are belowboundaries[0]or mapped to ncolors if they are aboveboundaries[-1]. These are then converted to valid indices byColormap.__call__.- extend{'neither', 'both', 'min', 'max'}, default: 'neither'
Extend the number of bins to include one or both of the regions beyond the boundaries. For example, if
extendis 'min', then the color to which the region between the first pair of boundaries is mapped will be distinct from the first color in the colormap, and by default aColorbarwill be drawn with the triangle extension on the left or lower end.
Notes
If there are fewer bins (including extensions) than colors, then the color index is chosen by linearly interpolating the
[0, nbins - 1]range onto the[0, ncolors - 1]range, effectively skipping some colors in the middle of the colormap.- __call__(value, clip=None)[source]#
This method behaves similarly to
Normalize.__call__, except that it returns integers or arrays of int16.