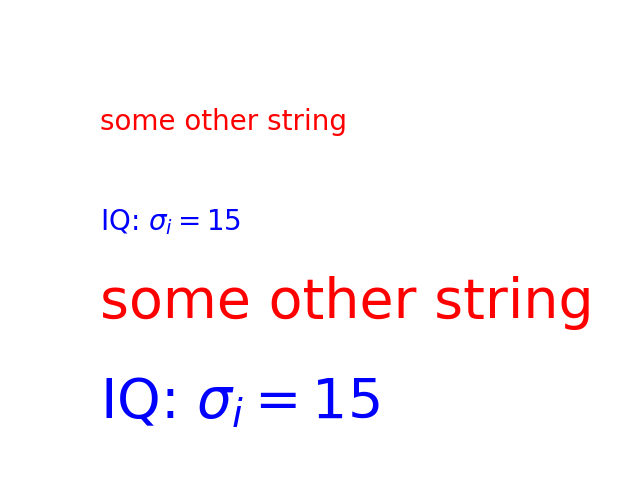Note
Click here to download the full example code
Convert texts to images#
from io import BytesIO
from matplotlib.figure import Figure
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.transforms import IdentityTransform
def text_to_rgba(s, *, dpi, **kwargs):
# To convert a text string to an image, we can:
# - draw it on an empty and transparent figure;
# - save the figure to a temporary buffer using ``bbox_inches="tight",
# pad_inches=0`` which will pick the correct area to save;
# - load the buffer using ``plt.imread``.
#
# (If desired, one can also directly save the image to the filesystem.)
fig = Figure(facecolor="none")
fig.text(0, 0, s, **kwargs)
with BytesIO() as buf:
fig.savefig(buf, dpi=dpi, format="png", bbox_inches="tight",
pad_inches=0)
buf.seek(0)
rgba = plt.imread(buf)
return rgba
fig = plt.figure()
rgba1 = text_to_rgba(r"IQ: $\sigma_i=15$", color="blue", fontsize=20, dpi=200)
rgba2 = text_to_rgba(r"some other string", color="red", fontsize=20, dpi=200)
# One can then draw such text images to a Figure using `.Figure.figimage`.
fig.figimage(rgba1, 100, 50)
fig.figimage(rgba2, 100, 150)
# One can also directly draw texts to a figure with positioning
# in pixel coordinates by using `.Figure.text` together with
# `.transforms.IdentityTransform`.
fig.text(100, 250, r"IQ: $\sigma_i=15$", color="blue", fontsize=20,
transform=IdentityTransform())
fig.text(100, 350, r"some other string", color="red", fontsize=20,
transform=IdentityTransform())
plt.show()
References
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown in this example: