Note
Click here to download the full example code
Resizing axes with constrained layout#
Constrained layout attempts to resize subplots in a figure so that there are no overlaps between axes objects and labels on the axes.
See Constrained Layout Guide for more details and Tight Layout guide for an alternative.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def example_plot(ax):
ax.plot([1, 2])
ax.set_xlabel('x-label', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('y-label', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('Title', fontsize=14)
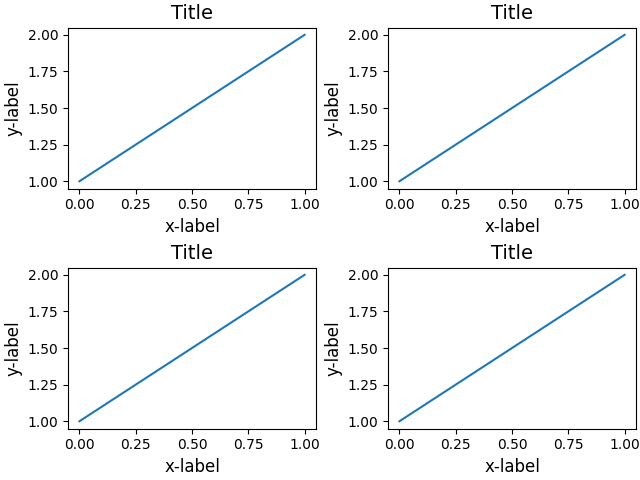
If we don't use constrained_layout, then labels overlap the axes
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, constrained_layout=False)
for ax in axs.flat:
example_plot(ax)
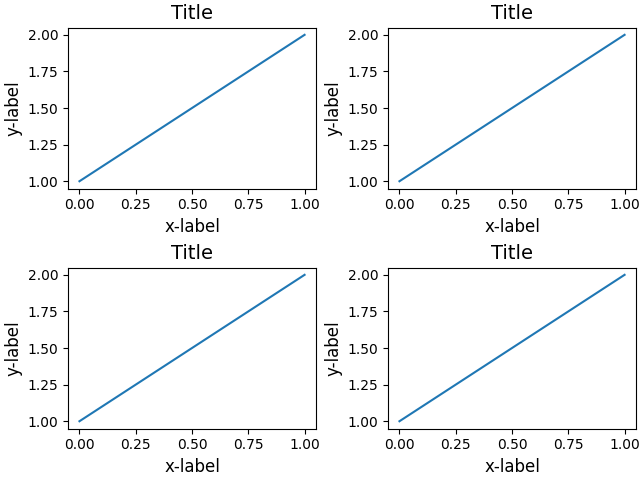
adding constrained_layout=True automatically adjusts.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, constrained_layout=True)
for ax in axs.flat:
example_plot(ax)
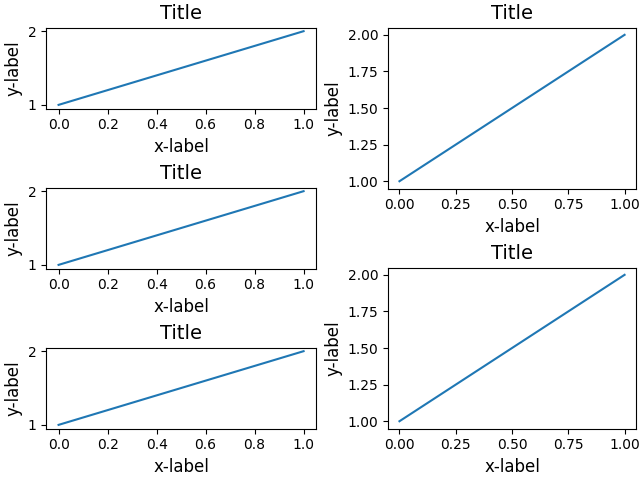
Below is a more complicated example using nested gridspecs.
fig = plt.figure(constrained_layout=True)
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
gs0 = gridspec.GridSpec(1, 2, figure=fig)
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpecFromSubplotSpec(3, 1, subplot_spec=gs0[0])
for n in range(3):
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs1[n])
example_plot(ax)
gs2 = gridspec.GridSpecFromSubplotSpec(2, 1, subplot_spec=gs0[1])
for n in range(2):
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs2[n])
example_plot(ax)
plt.show()
References
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown in this example:
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.712 seconds)