Note
Click here to download the full example code
Using accented text in Matplotlib#
Matplotlib supports accented characters via TeX mathtext or Unicode.
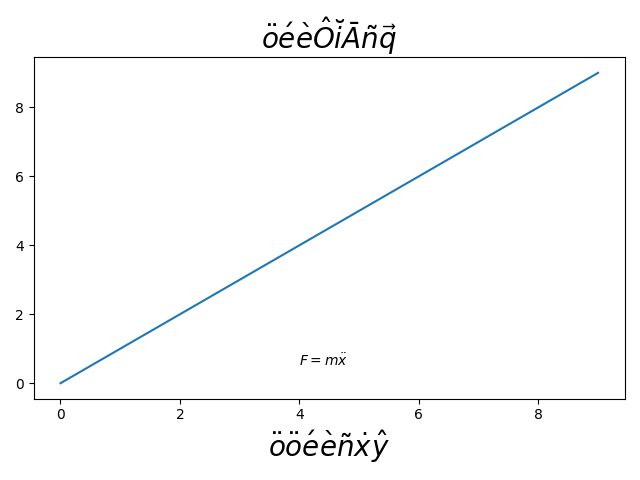
Using mathtext, the following accents are provided: \hat, \breve, \grave, \bar, \acute, \tilde, \vec, \dot, \ddot. All of them have the same syntax, e.g. \bar{o} yields "o overbar", \ddot{o} yields "o umlaut". Shortcuts such as \"o \'e \`e \~n \.x \^y are also supported.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Mathtext demo
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(range(10))
ax.set_title(r'$\ddot{o}\acute{e}\grave{e}\hat{O}'
r'\breve{i}\bar{A}\tilde{n}\vec{q}$', fontsize=20)
# Shorthand is also supported and curly braces are optional
ax.set_xlabel(r"""$\"o\ddot o \'e\`e\~n\.x\^y$""", fontsize=20)
ax.text(4, 0.5, r"$F=m\ddot{x}$")
fig.tight_layout()
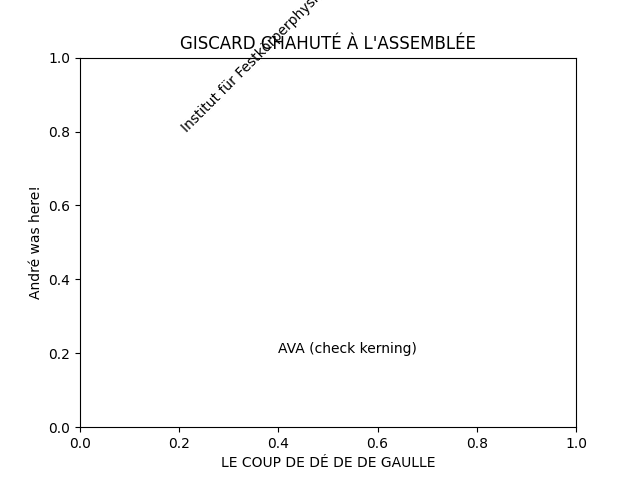
You can also use Unicode characters directly in strings.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title("GISCARD CHAHUTÉ À L'ASSEMBLÉE")
ax.set_xlabel("LE COUP DE DÉ DE DE GAULLE")
ax.set_ylabel('André was here!')
ax.text(0.2, 0.8, 'Institut für Festkörperphysik', rotation=45)
ax.text(0.4, 0.2, 'AVA (check kerning)')
plt.show()