mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator.zoomed_inset_axes#
- mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator.zoomed_inset_axes(parent_axes, zoom, loc='upper right', bbox_to_anchor=None, bbox_transform=None, axes_class=None, axes_kwargs=None, borderpad=0.5)[source]#
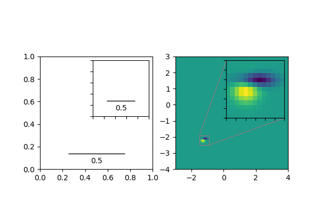
Create an anchored inset axes by scaling a parent axes. For usage, also see the examples.
- Parameters:
- parent_axes
matplotlib.axes.Axes Axes to place the inset axes.
- zoomfloat
Scaling factor of the data axes. zoom > 1 will enlarge the coordinates (i.e., "zoomed in"), while zoom < 1 will shrink the coordinates (i.e., "zoomed out").
- locstr, default: 'upper right'
Location to place the inset axes. Valid locations are 'upper left', 'upper center', 'upper right', 'center left', 'center', 'center right', 'lower left', 'lower center, 'lower right'. For backward compatibility, numeric values are accepted as well. See the parameter loc of
Legendfor details.- bbox_to_anchortuple or
matplotlib.transforms.BboxBase, optional Bbox that the inset axes will be anchored to. If None, parent_axes.bbox is used. If a tuple, can be either [left, bottom, width, height], or [left, bottom]. If the kwargs width and/or height are specified in relative units, the 2-tuple [left, bottom] cannot be used. Note that the units of the bounding box are determined through the transform in use. When using bbox_to_anchor it almost always makes sense to also specify a bbox_transform. This might often be the axes transform parent_axes.transAxes.
- bbox_transform
matplotlib.transforms.Transform, optional Transformation for the bbox that contains the inset axes. If None, a
transforms.IdentityTransformis used (i.e. pixel coordinates). This is useful when not providing any argument to bbox_to_anchor. When using bbox_to_anchor it almost always makes sense to also specify a bbox_transform. This might often be the axes transform parent_axes.transAxes. Inversely, when specifying the axes- or figure-transform here, be aware that not specifying bbox_to_anchor will use parent_axes.bbox, the units of which are in display (pixel) coordinates.- axes_class
matplotlib.axes.Axestype, default:HostAxes The type of the newly created inset axes.
- axes_kwargsdict, optional
Keyword arguments to pass to the constructor of the inset axes. Valid arguments include:
Property
Description
{'box', 'datalim'}
a filter function, which takes a (m, n, 3) float array and a dpi value, and returns a (m, n, 3) array and two offsets from the bottom left corner of the image
scalar or None
(float, float) or {'C', 'SW', 'S', 'SE', 'E', 'NE', ...}
bool
{'auto', 'equal'} or float
bool
unknown
unknown
Callable[[Axes, Renderer], Bbox]
bool or 'line'
float or None
bool
Patch or (Path, Transform) or None
facecoloror fccolor
bool
str
bool
object
bool
bool
unknown
None or bool or float or callable
[left, bottom, width, height] or
Bboxunknown
float or None
bool
(scale: float, length: float, randomness: float)
bool or None
str
str
bool
unknown
str
(bottom: float, top: float)
float greater than -0.5
unknown
unknown
unknown
unknown
str
(bottom: float, top: float)
float greater than -0.5
unknown
unknown
unknown
float
- borderpadfloat, default: 0.5
Padding between inset axes and the bbox_to_anchor. The units are axes font size, i.e. for a default font size of 10 points borderpad = 0.5 is equivalent to a padding of 5 points.
- parent_axes
- Returns:
- inset_axesaxes_class
Inset axes object created.
Examples using mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator.zoomed_inset_axes#
Adding a colorbar to inset axes